First solar wind data for JENI onboard JUICE!
On June 5, less than two months after the successful launch of the ESA spacecraft JUICE (JUpiter Icy moon Explorer) towards Jupiter, the Jupiter Energetic Neutrals and Ions (JENI) sensor led by APL Johns Hopkins University in the USA and part of the Particle Environment Package (PEP) instrument led by IRF Kiruna in Sweden was successfully switched on for its commissioning. JENI became fully operational on June 14, with all its systems running nominally for a few days. The first data obtained in the solar wind by the instrument demonstrated its very good scientific performances in flight as expected. Unique high-quality data are foreseen at Jupiter in a few years!
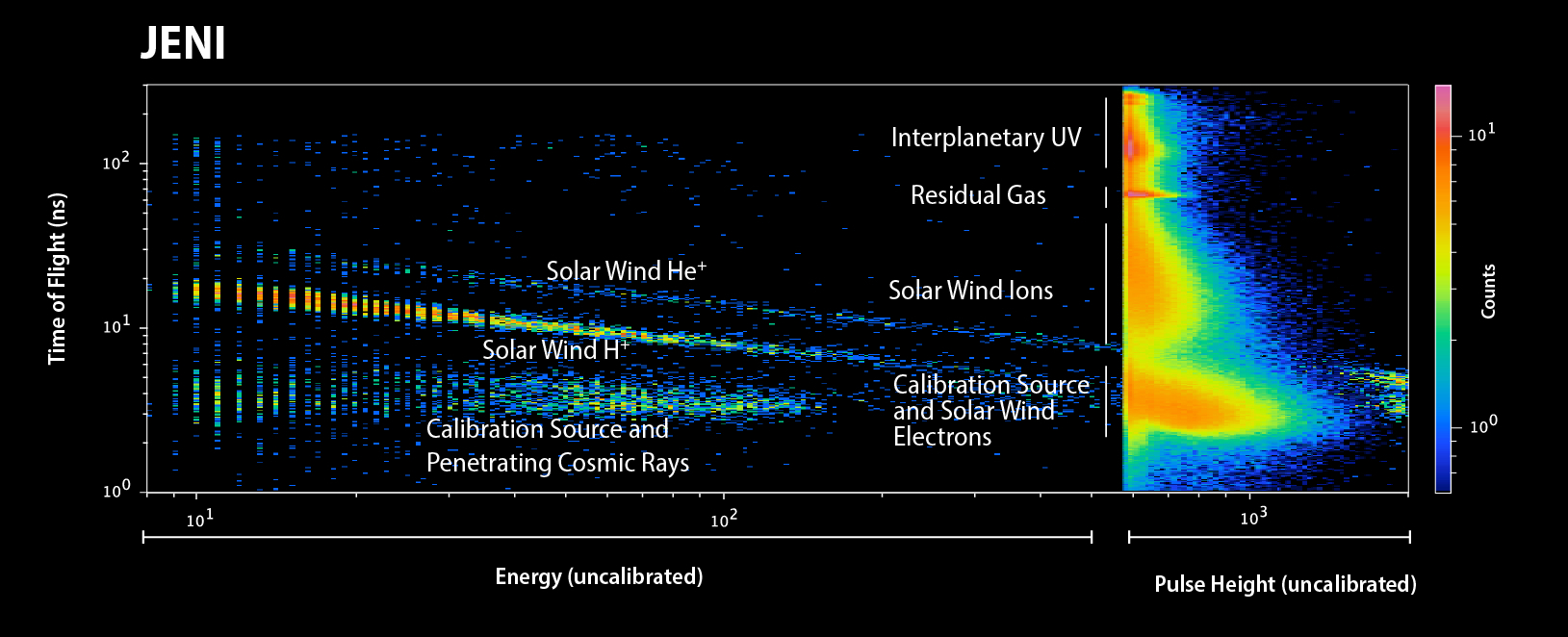
Observations obtained by JENI in the solar wind, showing on the left the SSD data with a mix of foreground solar wind protons and He+ ions (aperture open) and calibration source (aperture closed), and on the right the MicroChannel Plate (MCP) data with from top to bottom UV noise (precisely as predicted), proton line from residual gas in the MCP (will diminish over time), foreground solar wind ions (aperture open), calibration source (aperture closed), and solar wind electrons (aperture open). Credit: Johns Hopkins APL/Pontus Brandt. More info …
On July 3, the Particle Environment Package (PEP) instrument onboard the ESA spacecraft JUICE achieved a major milestone with the successful commissioning at low-voltage of all its six sensors, including the Jupiter Dynamic and Composition Analyzer (JDC) led by IRF Kiruna.Complete and more extensive functional tests at high-voltage will be performed in the coming months.
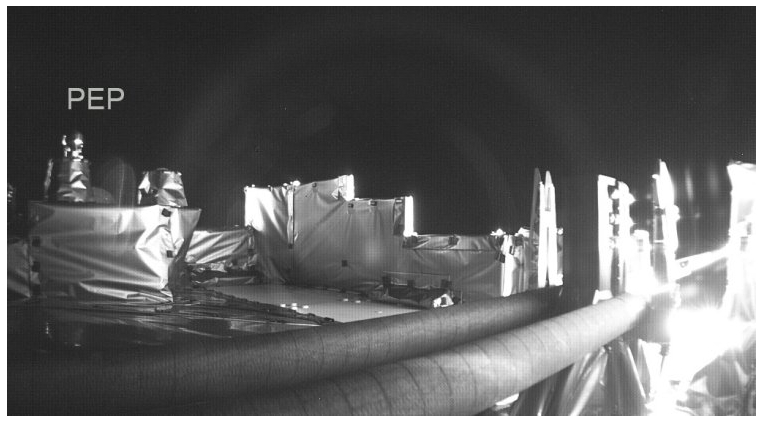
Three of the six sensors (NIM, JNA, and JEI) of the Particle Environment Package (PEP) taken from the side by the onboard camera of the ESA spacecraft JUICE. Caption: ESA/Juice/JMC, CC BY-SA 3.0 IGO. More info …
IRAP contributed to the JDC sensor for IRF Kiruna in Sweden by supplying its sweeping high-voltage power supplies, and to the JENI sensor for APL Johns Hopkins University in the USA by suppling and characterizing its Micro-Channel Plate (MCP) detectors. More info …
Further Resources
- JUICE, searching for life on Jupiter’s icy moons (Airbus Press Release)
- “Mars, la nouvelle odyssée : au-delà de la planète rouge” (2/6) : la revanche des lunes (Podcast FranceInfo)
- The making of Juice: the film (ESA)
IRAP Contact
- Nicolas André, nicolas.andre@irap.omp.eu
- Olivier Chassela, olivier.chassela@irap.omp.eu
- Rituparna Baruah, rituparna.baruah@irap.omp.eu






