IRAP delivers the control box for the Raman instrument on board the ESA ExoMars Mars rover
On June 25, 2024, the flight model of the Raman instrument control unit (RLS) was delivered to Thales Alenia Space Italia in Turin. This delivery follows the decision by ESA and CNES to take advantage of the postponement of the mission to 2028 to upgrade the instrument.
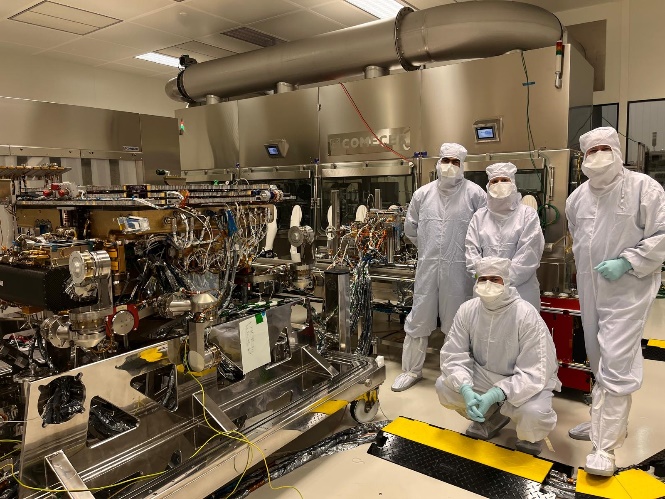

© ESA ExoMars Rosalind Franklin Mission (RFM)
The RLS (Raman Laser Spectrometer) instrument operates inside the rover. It analyzes powdered samples simultaneously with 2 other instruments, Micromega and MOMA. It studies the mineralogy of Mars using Raman spectroscopy, a well-known laboratory technique.

The box provided by IRAP controls all the instrument’s systems, in particular the focusing of the green laser (532 nm), the collection of Raman photons and their spectral analysis. It also handles command sequencing, data formatting and communication with the rover. Due to its size and the heat it generates, this 1 litre, 1 kg box was a real technological challenge to develop. It took 4 months to upgrade the electronics box, perform vibration and thermal vacuum tests, and validate the health of the instrument one last time. Finally, it was decontaminated to make sure it wouldn’t contaminate Mars!
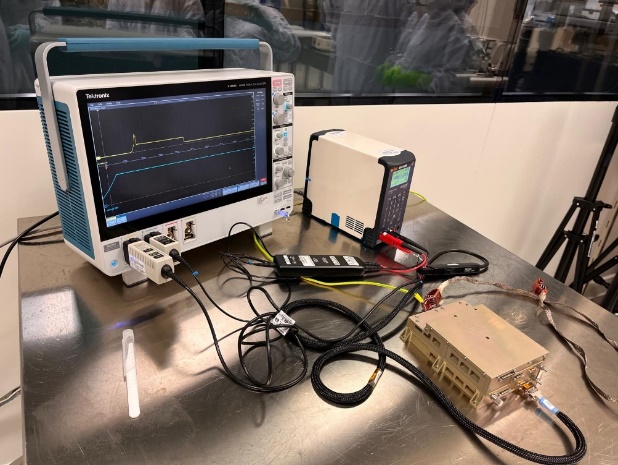
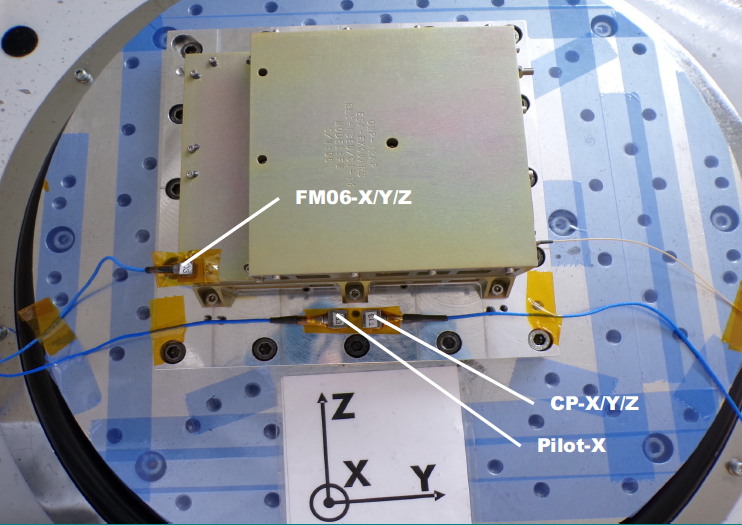

© ESA ExoMars Rosalind Franklin Mission (RFM)
Further Resources
- ESA Press Release : Laser upgrade for Mars rover
- IRAP’s contribution to the mission : ExoMars/RLS
- Mission sheet on the CNES website : Exomars / Rosalind Franklin
Contacts IRAP
- Yann Parot (IRAP), yann.parot@irap.omp.eu
- Sylvestre Maurice (IRAP), sylvestre.maurice@irap.omp.eu






