Two French instruments on the way to China
SVOM is a Franco-Chinese space mission dedicated to the study of the transient sky with a particular interest in gamma-ray bursts. SVOM will work in synergy with ground-based gravitational wave detectors to detect the electromagnetic counterparts of the coalescence of neutron star binaries and neutron star-black hole binaries.
SVOM will embark four instruments among which ECLAIRs and MXT, designed and built in France.
IRAP has built the detection scheme and the readout electronics of the ECLAIRs instrument and will manage the ECLAIRs instrumentation center which will take care of all operational activities once the instrument is in space. ECLAIRs will be responsible for autonomously detecting and providing the first localization of high energy transient events.
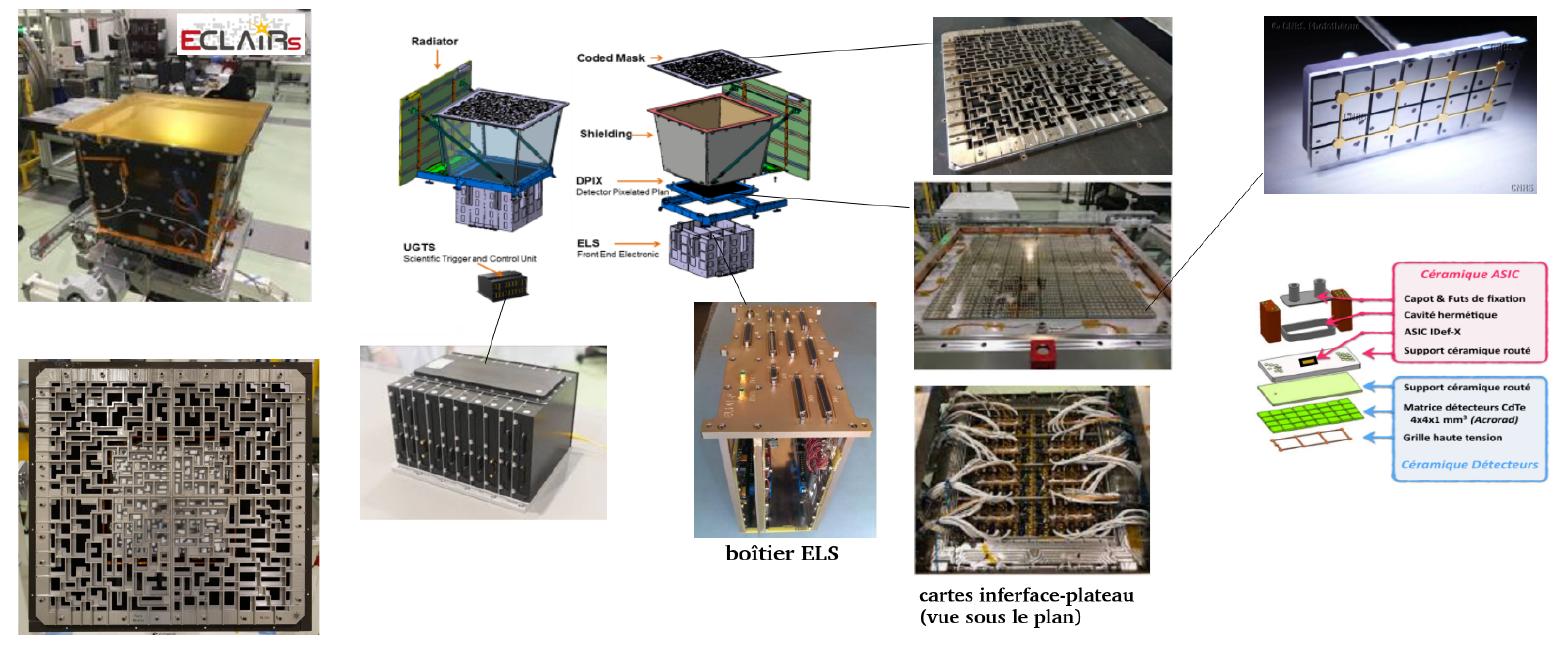
On Monday, the two French instruments ECLAIRs and MXT left CNES to be delivered to China (Shanghai). In total, two semi-trailers carry 24 containers for more than 8 tons of equipment.
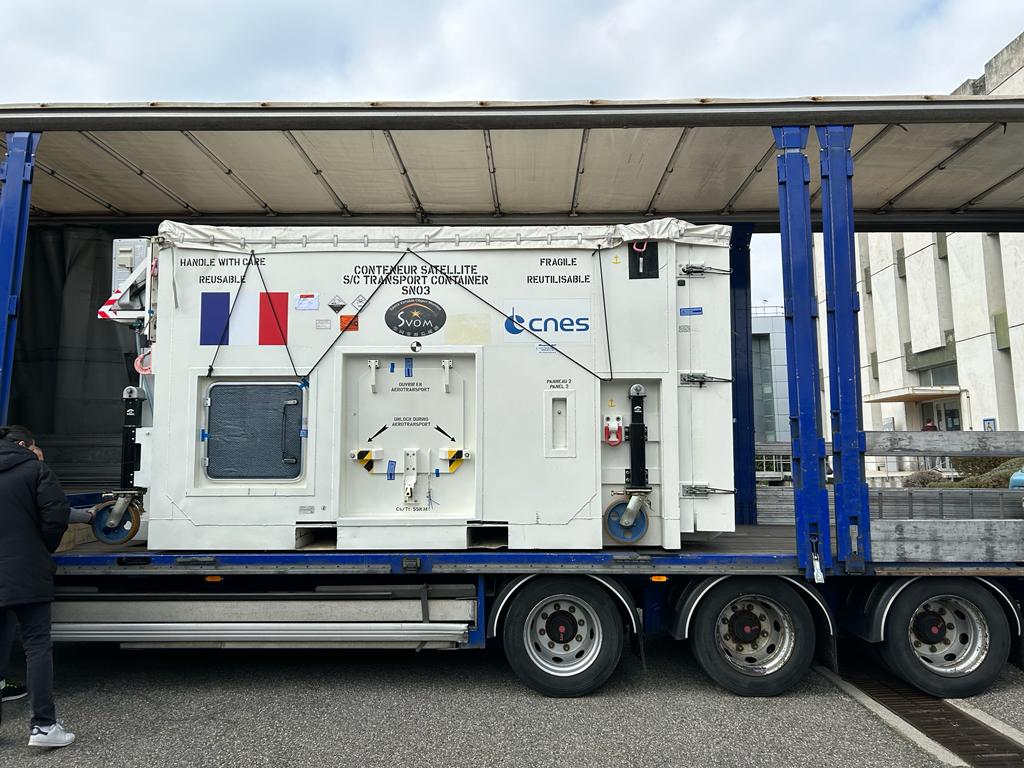

In China, the French instruments will be integrated into the dedicated platform. Then, the satellite as a whole will undergo several series of environmental and thermal vacuum tests.
See you in December 2023 for the launch of SVOM!
IRAP Contacts
- Jean-Luc Atteia, Jean-Luc.Atteia@irap.omp.eu
- Olivier Godet, olivier.godet@irap.omp.eu
- Sébastien Guillot, sebastien.guillot@irap.omp.eu
- Laurent Bouchet, laurent.bouchet@irap.omp.eu






