Massive stars make waves
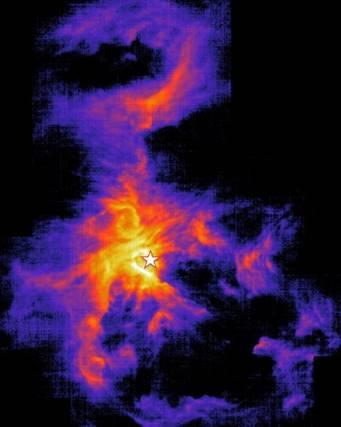
The Milky Way has about 100 billion stars, most of which were formed when our galaxy was half its current age. Over the time, the star formation rate has considerably slowed in our galaxy. CNRS researchers and their international colleagues1 provide a new explanation for this phenomenon by showing that stellar winds issued from massive stars disturb the gas clouds in which stars like the Sun form, slowing their formation. Using NASA’s SOFIA observatory, scientists mapped the “footprint” left by stellar winds on the gas clouds of the Orion Nebula (see image). In particular, they were able to measure the amount of energy deposited in the cloud with an unprecedented accuracy. These results reveal that the influence of stellar winds is even greater than that of supernovae, which are considered to be the most violent phenomena in the universe. The study is published on January 7, 2019 in the journal Nature.
1 Institut de recherche en astrophysique et planétologie (CNRS/Université Toulouse III Paul Sabatier), Institut de Radioastronomie Millimétrique, Leiden Observatory, Institute of Physics – University of Cologne, Instituto de Física Fundamental (CSIC), Telespazio Vega UK Ltd for ESA/ESAC, Universities Space Research Association/SOFIA, NASA Ames Research Center, Department of Astronomy – University of Maryland and Max-Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy.
Further Resources
- Article : Disruption of the Orion Molecular Core 1 by the stellar wind of the massive star θ1 Ori C. C. Pabst, R. Higgins, J.R. Goicoechea, D. Teyssier, O. Berne, E. Chambers, M.Wolfire, S. Suri, R. Guesten, J. Stutzki, U.U. Graf, C. Risacher, A.G.G.M.Tielens. Nature, le 7 janvier 2019. http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0844-1
- SOFIA Science Center Press Release : Lifting the Veil on Star Formation in the Orion Nebula
IRAP Contact
- Olivier Berné, olivier.berne@irap.omp.eu






