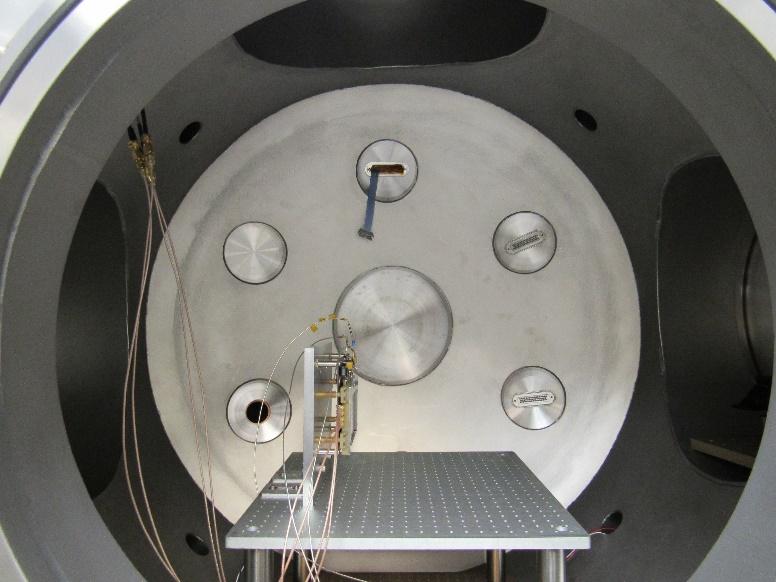
Delivery and testing of the first set of FM MCP detectors for the JENI instrument
On June 7, 2018, the JUICE (Jupiter Icy moon Explorer, European Space Agency) project team at IRAP went to the Applied Physics Laboratory (APL), Johns Hopkins University in Maryland, USA to deliver and test the first 6 MCP FM set of their JENI instrument (Jupiter Energetic Neutrals and Ions, instrument dedicated to the detection of energetic neutral and ion particles in the Jovian environment and in particular around the Galilean moons) for the instrument suite PEP (Particle Environment Package) and whose C phase transition of the design was validated during the NASA CDR held on June 12th and 13th. This delivery will be followed by two other complete MCP sets plus spares that will be delivered by this fall. IRAP’s contributions to the design of the APL’s instrument have consisted in the procurement and the characterization of the EM and FM MCPs. The lifetime and the differential gain degradation tests as well as the measurement of the gain of the MCPs as a function of temperature were performed in our CALIPSO 2 and CALIPSO 3 facilities located in the P2IS building on the Roche site which have been specially equipped for this tests. In addition to the tests we performed at IRAP, we also tested the MCP in a Van de Graaff generator at ONERA in Toulouse, France to evaluate their efficiency against radiation and measured their resistance in the temperature range -50 ° C to + 50 ° C using the installation of INTRASPEC in Toulouse. Figures 1 and 2 show the MCPs assembled on their support and installed in the test bench of the APL.